NICE RPA Deepens AI Capabilities for Expanded Automation Discovery and Real-Time Monitoring
NICE has updated its Robotic Process Automation with more AI-based features to promote more rapid automation development, efficient robotic and human workforce management and to better ensure business continuity.
NICE has updated its Robotic Process Automation with more AI-based features to promote more rapid automation development, efficient robotic and human workforce management and to better ensure business continuity.
Notable capabilities in NICE RPA version 7.1 include identifying sub-processes, proactive identification of automation workflows and connectivity issues, intelligent real-time data, dashboards and sophisticated control features.
With its approach to RPA, NICE aims to empower organizations to make smarter decisions based on advanced analytics of structured and unstructured data, according to Barry Cooper, the president of NICE Enterprise Group.
NICE RPA version 7.1’s “innovative new capabilities across all stages of the automation lifecycle enable our customers to automate easier, faster, and with even more impressive results, he added in a statement.
These are among some notable NICE RPA 7.1 updates that illustrate lifecycle improvements:
- Automation Discovery Phase: This aims to help organizations plan and develop their automation roadmap, increase the footprint, and speed up ROI for automation investments.
- Automation Development Phase: To help IT deploy RPA solutions error-free as quickly as possible, Nice RPA 7.1 is equipped with a new built-in debugger capability, which shows a detailed view of the automation development flow just with a touch of a button. With this, developers can pinpoint issues within the automation flow and resolve them quickly.
- Operationalization Phase: The NICE Employee Virtual Attendant (NEVA) NEVA sports a human-like that “personifies how the human and robotic workforces can work together collaboratively,” according to the company. NEVA actually invites employees to request assistance and ask questions. In turn, employees can ask NEVA to execute a task as needed. NEVA can also integrate with any desktop application, legacy system, and virtual environment.
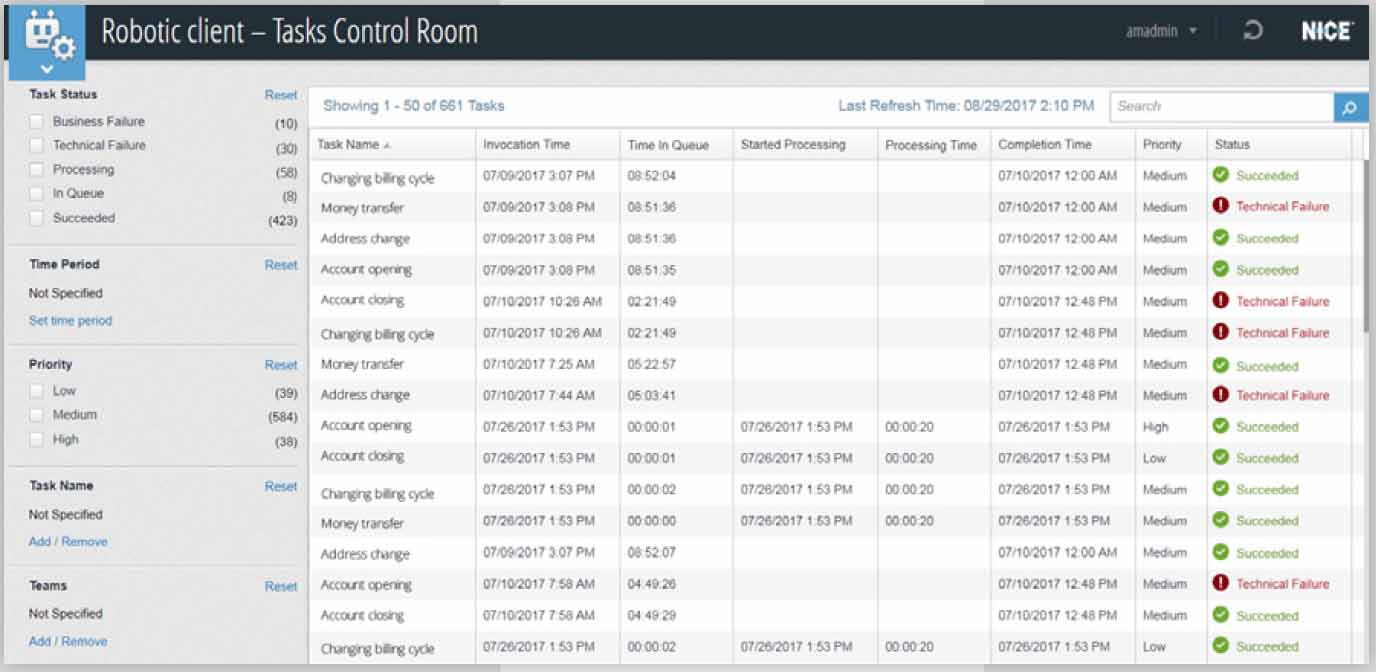
- Maintenance and Monitoring Phase: A number of additions help administrators to seamlessly monitor and control the robotic workforce at scale while taking decisive action in real-time. The capabilities of the Connectivity Watcher have been expanded so that administrators are alerted in real-time as connectivity breaks occur.
Inside the Nice RPA – Components and Capabilities
The NICE Virtual workforce comprises of software robots that are installed on back-end servers, with the capabilities to take over all the repetitive, admin driven processes facing the human workforce every day.
A variety of tasks can be executed independently without human intervention, freeing up employees to focus their attention on more valuable business priorities.
Enterprises using RPA find the enjoy the most ROI for both IT and business when the use it across their front office, back office, and shared services divisions, Cooper noted.
Among the most mentioned benefits from NICE robotic automation are:
Increase throughput: Robots are 4-5 faster than humans and work 24/7
Ensure compliance: Robots deliver results with 100% accuracy
Reduce costs: 10 robots can do the work of 100 people
Increase employee engagement: let employees focus on the value-add activities
Easily scalable: As your enterprise grows, you can scale up the power of Robotic Automation to match your changing needs
NICE Marries RPA and AI To Improve Interfaces, Deliver Built-In Intelligence
NICE’s efforts to marry RPA with AI really got going with the major release of NICE 7.0, where the company targeted ways to use RPA-AI to support intelligent process selection and production speed.
In his blog, Oded Karev, NICE vice president for advanced process automation solutions described NICE’s view of RPA-AI in detail. In part, he wrote.
A common industry pain point, felt by many organizations globally, is deciding which business processes should be automated and which criteria to follow while evaluating process candidates for automation.This essential building block in the RPA and Desktop Automation life-cycles can determine the success or failure of an RPA project. Automation Finder is a home-grown AI infused RPA diagnostic tool, unique to NICE, and designed to pinpoint the specific processes which are ripe for automation, with precision and speed utilizing Desktop Analytics, Machine Learning and Deep Learning technologies.
[NICE] Version 7.0 enables organizations to leverage Automation Finder to its full potential. Additionally, processes which are selected by Automation Finder which are suitable for both unattended and attended automation, will by default yield the greatest ROI for the organization.
The phase of designing or developing process automations is fraught with challenges from sourcing automation developers with the right level of experience, to establishing the right connectivity and all the while ensuring that the business users will successfully adopt the automated process.
Automation Studio, a next generation, cloud-based design environment for creating and managing automations will curb many of these challenges. The user-friendly UI, along with its built-in intelligence, provides a unique and simplified approach for automation design, which enables less technical users to create and develop process automations.The built-in intelligence feature offers real-time guidance to the developer, as they are designing the automation to ensure successful deployment. This enables faster production, with minimal design errors, ultimately enabling organizations to reduce the time to value gap with faster ROI realization. What’s more, with fully enabled continuous delivery from the cloud, new features and capabilities can be accessed immediately, as and when they first become available. This enables automation developers to enjoy the latest features without having to undergo a full upgrade.
This push to deliver a better interface to RPA is driven in large part by what Karey called ‘the Human2Robot’ Interaction. The updates for NEVA (NICE Employee Virtual Attendant) “personifies how the human and robotic workforces can work together collaboratively.”
Karev shared more details on the nature of this new-gen interface thinking:
NEVA's intuitive human-like interface invites employees to request real-time assistance and ask questions via text. Employees can ask NEVA to execute a task, perform calculations or display contextual process guidance as and when they need it. Essentially revolutionizing the way in which processes are automated and optimized on the Desktop, NEVA can also trigger the unattended robotic workforce, in the backend, to execute various processes.
NICE 7.x also sports a Unified Admin, which lets human employees track, monitor and manage to monitor and manage their entire robotic workforce from a single screen view.







